VIRUS CONTACT TRACING
Virus contact tracing is the process epidemiologists are now using (as of August 2020) to shed light on how the coronavirus (COVID-19) is spread. But this is not by any means a new process.
The first instance when virus contact tracing was used occurred during the cholera epidemic in the 19th century in England largely through the efforts of a young doctor by the name of John Snow.
CHOLERA
Cholera is a dreadful disease. It causes diarrhea so severe that a victim can lose as much as ten liters of water in a day. If untreated, it can lead to rapid dehydration and death within a few days.
The disease first appeared in Europe in 1831. It was carried from the Indian subcontinent where it was endemic. Over 50,000 Britons died within 1 year, causing widespread panic.
Physicians did not know what to do. They plied their patients with arsenic and strychnine, administered tobacco enemas, wrapped their patients in flannel soaked in turpentine, bled their patients with leeches and blistered them with nitric acid. All, of course, to no avail.
No one knew what caused the disease, but the prevailing opinion was that cholera was somehow transmitted by bad air, or a ‘miasma’ that emanated from the sick and from garbage. A London dentist claimed that the solution was to fire cannons every hour to disperse the bad air!
DR. JOHN SNOW
Dr. John Snow was a young apprentice doctor at the time of the epidemic and attended to many of the cholera victims himself. He didn’t buy the idea of poisoned air. It seemed clear to him that cholera was due to some poison that acted directly on the intestines and therefore was most likely introduced through the mouth.
His suspicion turned to water when he noted that the city of Birmingham had been spared of cholera. What was the difference here? Nobody drank river water. It was so foul that nobody could stomach it. People in Birmingham drank only well water.
DR. SNOW'S THEORY OF HOW CHOLERA IS SPREAD
By 1849, Snow had published a pamphlet suggesting that cholera was spread by water, but his ideas were largely ignored.
His views were looked down upon because he had been trained through apprenticeship rather than through one of the Royal Colleges and was thus not considered a member of the establishment.
Most prominent physicians did not want their theories about miasmas disturbed, and in any case, by 1849, the epidemic had waned.
1854-A NEW CHOLERA OUTBREAK
IN LONDON
In 1854, Snow got his chance to prove his theory. A terrible cholera epidemic broke out in London, centered in the Soho district where more than 500 people died within ten days in an area of a few city blocks.
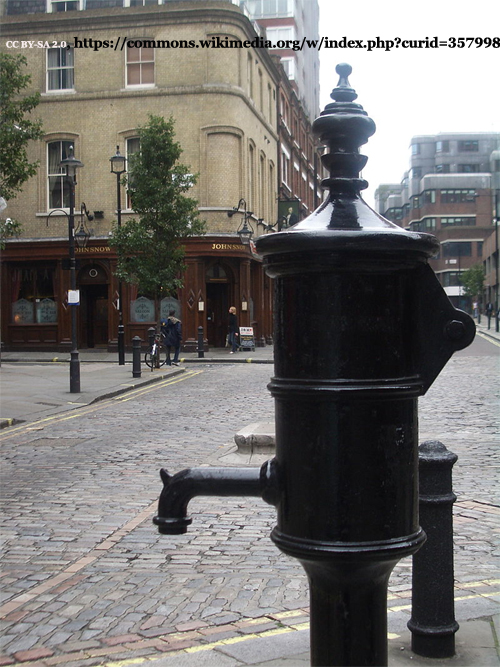
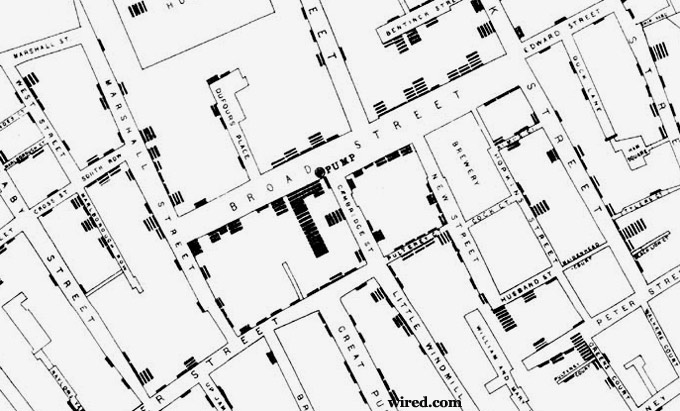
Dr. Snow took a map of the city and laboriously plotted out the location of houses where someone had come down with cholera. An amazing pattern was revealed. The red dots, signifying cholera cases clustered around a major thoroughfare then known as Broad Street. What on this particular street could be causing cholera, Snow wondered? He soon found the answer.
A water pump that supplied the neighborhood sat right in the area pinpointed by the dots on his map as the focal point of the epidemic. He quickly discovered that seven men who lived outside Soho but had worked in the area around the pump all died of cholera and that a widow who had just moved away from the neighborhood to Hampstead, but had sent for some of the water she had been accustomed to drinking, also had died. But perhaps the most convincing observation Snow made was that in a nearby brewery, (where the workers never drank water) not a single worker came down with cholera!
THE CLUE TO THE CAUSE OF THE BROAD STREET EPIDEMIC
At this point Snow approached city officials, showed them his map, and suggested that the handle of the pump in Broad Street be removed as a public health measure.
Legend has it that this immediately stopped the epidemic. The actual fact is that by the time the pump handle was removed, the number of new cholera cases had slowed to a trickle.
Snow did not single-handedly stop the cholera epidemic as the myth suggests, but that in no way diminishes his accomplishment. He clearly showed that cholera could be transmitted by polluted drinking water and went on to demonstrate that sewage was the culprit.
DR. SNOW'S LEGACY
The Broad Street epidemic was eventually traced to a baby with diarrhea whose mother had washed diapers in water that was dumped in a cesspool that leaked into the well supplying the pump.
Snow went on to show that cholera was far more prevalent in homes supplied by a water company that took its water from near London Bridge than one that drew it from further up the river.
By 1855 he had clearly shown that the disease was caused by some infectious agent in the water and his book published that year, ‘On the Mode of Communication of Cholera,’ stands as the groundbreaking work that eventually led to the chlorination of drinking water and the saving of millions of lives.
Dr. Snow’s solving the mystery of the transmission of cholera can be attributed to his pioneering effort at contact tracing, the same process that epidemiologists are now using to shed light on how the SARS-CoV-2 virus is spreading.
Much of the information for this article was provided by written permission of the McGill Office for Science and Society.
"The Cleanest Clean You've Ever Seen."
by
ABC Oriental Rug & Carpet Cleaning Co.
130 Cecil Malone Drive Ithaca, NY 14850
607-272-1566